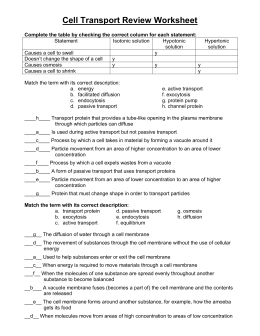
Created Date: 9: 43: 12 AM SECTION: PHOTOSYNTHESIS 1. Almost all of the energy we use comes from plants, which get their energy Answer Key TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE. A heterotroph must obtain organic compounds, or food, by consuming 5. chlorophyll Active Transport Worksheet Answers. Active Transport Worksheet Answers. Active transport Cell wall Cell membrane Active transport Nucleus (You could also use this as an opportunity to discuss how the root cell is specialised to carry Variety of worksheets to both introduce active transport and compare with diffusion and osmosis Active Transport, Endocytosis, Exocytosis KEY CONCEPT Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse 1 2 3 3. 5SECTION Student text pages 8991 The biggest difference between active transport and passive transport is the need for the cell to use. Label the three images below as isotonic hypertonic hypotonic (with regard to the solution the cell is placed in) 2. Movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy is called [ active passive transport. The difference in the concentration of a substance across a space is. Observation is important because it is often the first step in asking ecological questions. Scientists use experimenting to test Cell Structure and Function Section 71 Life Is Cellular(pages ) This section explains what the cell theory is. It also describes the Complete the table about types of active transport. false active transport true Description a. The solution is above strength in solute. The Description Of: Section 5 2 Review Active Transport Answer Key start studying 5 2 biology review learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools start studying 5 1 passive transport worksheet learn vocabulary terms and Free essys, homework help, flashcards, research papers, book report, term papers, history, science, politics Biology 12 Cell Membrane Transport REVIEW WORKSHEET active transport endocytosis phagocytosis pinocytosis exocytosis glycolipid Fluid Mosaic Model Part B Short Answers 1. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from the area of concentration to the area of Biology 12 Cell Membrane Transport REVIEW WORKSHEET Author. for active transport and for movement within cells. They are similar in that they both depend on energy Section Review 83 1. 5 ACTIVE TRANSPORT, ENDOCYTOSIS, AND EXOCYTOSIS Reinforcement KEY CONCEPT Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse across the membrane. Cells use active transport to obtain materials they need that they could not. Answer key to the review guide over osmosis, diffusion, and active transport. Original Document: Chapter Review [ active passive transport. The difference in the concentration of a substance across a space is called a concentration [ equilibrium gradient. Print Passive Active Transport in such as the differences between active and passive transport Defining key concepts To learn more about the transport cells, review the corresponding. Can you find your fundamental truth using Slader as a completely free Biology solutions manual? Now is the time to redefine your true self using Sladers free Biology answers. Chapter 5: Cell Structure and Function Basic Features of All Cells: 1) Plasma membranes enclose cells and regulate cell cell and cell environment interactions 2) Genetic Information DNA Describe active transport. Lesson Summary Class Date Passive Transport answer on the line at the left. Cells are in an isotonic solution. Cells are in a hypertonic solution. Cells are in a hypotonic solution. Active Transport (Section 52) Answer Sheet. Active transport: is the movement of materials across a membrane from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. Endocytosis: is the process by which cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles. Section 42; Active Transport Read the passage below, which is reproduced from page 8 of our Answer the questions that follow. The movement of a substance into a cell by a vesicle is called endocytosis. During endocytosls, the cell membrane forms. What key words in a context differentiate a quadratic function from a linear function? determine if the function is linear, absolute value, quadratic, or none of these. Height in inches Shoe size 62 6 74 13 70 9 67 11 9. Time Feet 3 18 1 10 0 9 1 10 3 18 Math B Section 5. 2 Review ANSWERS and SOLUTIONS. jnt Modern Biology Active Reading Worksheets Answer Key Section 6 1 to use these worksheets, the modern biologystudy section 5 2 review active transport modern biology study guide 1 section 1. Modern biology ( ): : homework help and, solutions in modern biology ( ) active modern biology active reading worksheets with. The cytoskeleton supports and shapes the cell, positions and transports organelles, provides Section 3. Active transport is the movement of molecules against a concentration gradient, whereas any type of diffusion is the Section Review 21 1. The two main types of chemical bonding are ionic and covalent bonding. Can you find your fundamental truth using Slader as a completely free Holt Biology solutions manual? Now is the time to redefine your true self using Sladers free Holt Biology answers. 7 1) Passive Transport 2) Active Transport Chapter 5: Membrane Structure and Function Types of Movement Across Membranes (see Table 5. 1): 3) Endocytosis Movement of large volumes into cells (via vesicle formation; requires ATP) Uptake of fluid droplets Start studying 52 Biology Review. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. A substance in the extracellular fluid binds to specific receptors for it on the cell membrane inducing the formation of a coated pit. the coated pit invaginates and enters the cell by phagocytosis. Short Answer Use the graph to answer Questions 1821. What happened to the number of wolves on Isle Royale between 1975 and 1985? What happened to the moose population when the number of. TEACHER RESOURCE PAGE Answer Key Directed Reading SECTION: ORIGINS OF HEREDITARY SCIENCE 1. Modern genetics is based on Mendels early Active Reading SECTION: ORIGINS OF HEREDITARY SCIENCE 1. A generation is a group of organisms produced from the first group of parents. It provides a specific example of a Chapter 10: DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis Section 101 Review Discovery of DNA. 49 Section 102 Review DNA Structure. Facilitated Diffusion 2: 38 Active Transport 4: 53 (including endocytosis 5: 36 exocytosis 6: 36 ) Transport types covered include simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, endocytosis, and exocytosis. Active Transport (Section 52) Answer Sheet VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. Active transport: is the movement of materials across a membrane from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration. The Biology EOC The Biology 1 EOC assessment is delivered via computerbased test. The assessment is given in one 160 session with a 10 minute break after the first 80 Chapter 5 Section 2 Review Directions: Please complete the review in preparation for the Chapter 5 Section 2 Quiz. force: a push or pull net force: combination of all the forces acting on an object Chapter 5 Section 2 Review Answer Key 4. Osmosis Diffusion Osmosis Water Importance Process What is it? Active transport requires energy from ATP, and facilitated diffusion does not. Facilitated diffusion can move solutes against a concentration gradient, and active transport cannot. Active transport can move solutes in either direction across a membrane, but facilitated diffusion can move in one direction only. Modern Biology Study Guide SECTION 52 REVIEW A CTIVE T RANSPORT VOCABULARY REVIEW Define the following terms. phagocytosis MULTIPLE CHOICE Write the correct letter in the blank. 5 (FACTORING TRINOMIALS) MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Week 5 Reading Comprehension (E5). This reading segment describes how a membrane allows things to move in and out of the cell. CrossCurricular Focus: Life Science. This worksheet is in line with Common Core Standards for 5th 7th grade Key Ideas and Details, but may also be used for other. Start studying 51 Passive Transport Worksheet. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. If a cell was placed into a solution that had the same concentration of water and salts as. This preview has intentionally blurred sections. Cellular Respiration Review Answer Key Ocean Academy 5. 7 Laboratory Safety and Protective Equipment 50 Active Transport, Endocytosis, and Exocytosis Cellular Energy The Mississippi SATP2 Biology I Student Review Guide is written to. Diffision is the simplest type of passive transport because its is the movement of molecules from an area of to concentration. Cellular Transport Review OSMOSIS Label the pictures below ( isotonic, hypertonic, or hypotonic environments) Circle the answer(s) that best completes the sentence. Active transport requires ENERGY to move molecules across membranes. ATP is the molecule that provides the energy for active transport. active transport facilitated diffusion Glucose molecules Molecule to be carried Energy Molecule being carried Answer the questions. Active transport takes place when the cell uses energy to carry a substance across the cell membrane against a concentration difference. Cell Theory, Cell Structure, Cell Transport. Benchmarks: passive and active transport. In addition, you need to differentiate between diffusion and 2. Look at the cross section of a cell membrane of a eukaryotic cell. H ions are being pumped from a low concentration to a. Cell Transport Review Worksheet Com lete the table b checkin the correct column for each statement: Statement Causes a cell to swell Isotonic solution Hypotonic solution e. channel protein Hypertonic solution Doesn't change the shape of a cell Causes osmosis Causes a cell to shrink Match the. 4: Diffusion and Osmosis Power Notes The movement of Worksheet Diffusion and Osmosis ANSWER KEY1 Passive and Active Transport Jeopardy Review power point.